Coenzyme Q10 deficiency Symptoms
Understand how CoQ10 deficiency affects energy, heart & brain function, and discover effective testing methods and treatments to restore balance.
Are you perpetually exhausted and experiencing mysterious muscle weakness or unusual heart issues? Your body shows crucial indicators of a Coenzyme Q10 (CoQ10) deficiency. Among the compounds found in every human cell, CoQ10 operates as the basic power system that enhances cellular energy.
Decreased CoQ10 levels produce multiple subtle symptoms within the body, which create conflicting diagnostic challenges for healthcare workers and patients. CoQ10 deficiency symptoms need understanding because this medical condition presents itself through regular fatigue or age-related complaints that people frequently overlook.
The concerning aspect of CoQ10 deficiency is that it affects the heart, muscles, and brain at the same time. Stay put and learn about the health implications of this essential deficiency while understanding available treatment options.
Key Takeaways
- Multiple symptoms, such as intense fatigue and heart rhythm irregularities, can appear due to CoQ10 deficiency, which may negatively impact one's quality of life unless appropriately treated.
- Evaluating coq10 deficiency symptoms at their onset remains vital because medical professionals can successfully manage this condition through monitored supplemental intake alongside lifestyle improvements.
- Blood tests measure CoQ10 levels to deliver accurate diagnoses, enabling healthcare providers to create specific treatment options combining oral therapy with dietary modifications.
- People with risk factors for secondary CoQ10 deficiency should get regular monitoring because aging alongside certain medications, including statins and specific medical conditions, contributes to this deficiency.
What is Coenzyme Q10?
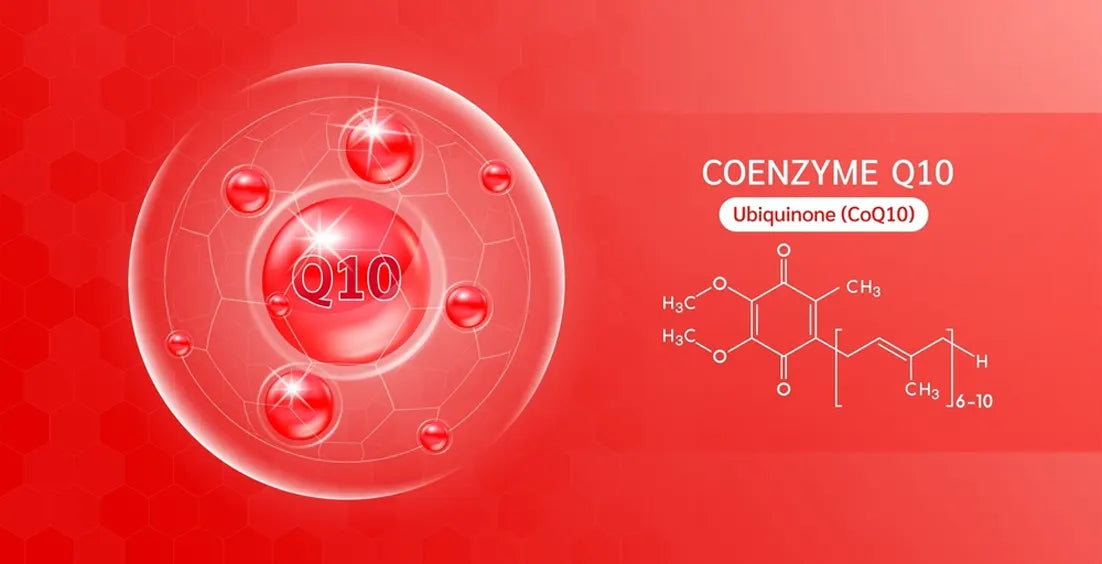
Coenzyme Q10 (CoQ10), or ubiquinone, is a fat-soluble molecule crucial for energy production within cell membranes. The body produces this essential quinone naturally to support cellular respiration by enabling electron transfer for ATP production.
CoQ10 safeguards cellular membranes and lipoproteins through its potent antioxidant activity while completing its fundamental function in energy metabolism. Human bodies produce CoQ10 primarily independently, while liver, heart, oily fish like sardines and mackerel, and whole grains serve as dietary sources.
Read More: Health Benefits of Coenzyme Q10
Signs or Symptoms of coq10 deficiency
Physical Fatigue and Muscle Weakness
CoQ10 deficiency typically begins with persistent physical fatigue that refuses to resolve even with adequate rest. Muscle weakness can occur during normal activities such as stair climbing and grocery carrying. Muscle tissues that require substantial energy depend heavily on CoQ10 for cellular energy generation, which results in this weakness.
Cardiovascular Complications
Symptoms involving the heart need immediate medical assessment to detect severe coq10 deficiency. Cardiovascular signs include an irregular heartbeat, increased blood pressure, and chest discomfort. Cardiovascular issues stem from the heart's need for CoQ10, as its optimal functioning organ requires high energy levels.
Cognitive Changes and Anxiety
Patients experiencing coq10 deficiency and anxiety report mental confusion together with problems focusing. Proper brain functioning requires significant energy consumption, and declines in CoQ10 concentrations result in reduced cognitive abilities. Research studies have steadily recognized the relationship between low coq10 levels and anxiety development.
Vision and Eye Problems
Coq10 deficiency dry eyes symptoms often appear in individuals together with vision-related complications. Your eyes need plenty of energy to function correctly, so they remain vulnerable to CoQ10 deficits. Light sensitivity alongside chronic eye strain frequently causes symptoms in people.
Sleep Disturbances
Coq10 deficiency insomnia creates a direct impact on sleep quality. Your ability to sleep and keep your eyes closed throughout the night could become hindered. The body requires CoQ10 to control energy cycles and cellular repair systems during sleep.
Statin-Related Symptoms
The medications used to lower cholesterol levels lead to specific coq10 deficiency symptoms from statins among users. Muscle pain increases alongside weakness and fatigue when coq10 deficiency develops. Statins decrease CoQ10 production in the body, which results in secondary coenzyme q10 deficiency.
Headaches and Migraines
A decline in CoQ10 levels reveals itself through more prevalent recurrent headaches or migraines. CoQ10 plays a protective role against inflammation in brain tissue while enabling cellular energy production between cells.
Gum Disease and Oral Health Issues
Your oral health can exhibit unexpected signs of coq10 deficiency. Good dental care does not protect against repetitive gum issues, which could lead to low CoQ10 levels and reduce tissue healing capability.
Temperature Sensitivity
Your body may begin showing sensitivity to heat or cold amounts throughout your extremities. The regulation of cellular energy production by CoQ10 influences temperature control in the body.
Hearing Loss
Patients with primary genetic CoQ10 deficiency may experience severe hearing problems due to progressive hearing impairment. Insufficient CoQ10 levels create an energy deficit in the inner ear that weakens hearing abilities as time passes.
Intellectual Disability and Development Issues
In severe cases, CoQ10 deficiency during early development of infancy can lead to intellectual disability. People with this condition present developmental delays combined with learning difficulties and cognitive challenges. The symptom primarily appears in individuals with primary coenzyme Q10 deficiency due to hereditary factors.
Kidney Dysfunction
Kidney function suffers due to CoQ10 deficiency because these organs use extensive energy levels to filter blood and manage fluid equilibrium. Patients may observe urinary changes and swelling throughout their bodies, along with irregular kidney test results. Kidney issues create serious health problems because they lead to other systemic complications.
Seizures
Individuals with primary CoQ10 deficiency often develop seizures alongside their condition. Brain cells need adequate energy production to function appropriately, and CoQ10 supports this process. Individuals with seizure symptoms have varying experiences.
What causes coenzyme q10 deficiency
Genetic Factors
People may possess genetic mutations that interfere with their ability to produce or use CoQ10. An inherited coenzyme Q10 deficiency presents itself early in life and generates severe symptoms. Multiple organ systems suffer impairment when genetic mutations disrupt body functions related to CoQ10 synthesis and usage.
Medication-Induced
Statin drugs prescribed to manage cholesterol levels cause the majority of coenzyme Q10 deficiency symptoms. Medications trigger the blockade of CoQ10 synthesis pathways, reducing CoQ10 production. Secondary coenzyme Q10 deficiency gradually occurs after patients begin taking statins.
Age-Related Decline
The natural aging process makes it harder for the body to create sufficient amounts of CoQ10. CoQ10 production diminishes substantially after age 40 and decreases further as individuals age. The natural decline of CoQ10 produces diverse symptoms, which mainly affect fatigue levels and muscle function.
Chronic Medical Conditions
Several health problems trigger and enhance CoQ10 deficiency. People with diabetes, heart disease, and cancer develop increased CoQ10 needs while experiencing issues with both CoQ10 production and usage. Medical conditions tend to accelerate CoQ10 depletion within the body.
Nutritional Deficiencies
Insufficient intake of CoQ10-rich foods causes CoQ10 deficiency. The human body forms CoQ10 naturally but needs food sources to keep its levels healthy. Inadequate consumption of CoQ10 occurs when diets restrict proper nutrition.
Mitochondrial Disorders
Mitochondrial conditions lead to substantial reductions both in CoQ10 content and its processing capacity. Symptoms of CoQ10 deficiency frequently develop due to its essential role in generating energy within mitochondria.
Oxidative Stress
Environmental stress combined with unhealthy life choices or illness rapidly lowers CoQ10 levels through excessive oxidative damage. The antioxidant properties of CoQ10 lead to depletion when the body requires more than it can produce.
Metabolic Demands
Intense physical activity and illness lead to CoQ10 depletion because they increase metabolic demands. A deficiency of CoQ10 occurs when body energy requirements surpass the capacity for CoQ10 production.
Reproductive Health
Female fertility and reproductive health require the essential action of CoQ10. Lowered CoQ10 levels during aging affect ovarian function and egg quality in women. Women over 35 who attempt to become pregnant require CoQ10 due to its support for egg mitochondria.
Menopause Management
Menopausal women experience natural CoQ10 reduction together with hormonal alterations. Sustained CoQ10 levels during these life changes might assist in managing overall transition effectiveness.
How to test for CoQ10 deficiency
Different medical methods exist to diagnose CoQ10 deficiency in patients. Blood assessments are the primary testing method, evaluating CoQ10 levels in blood plasma or serum. A healthcare professional will order a comprehensive metabolic panel with the CoQ10 analysis to monitor overall patient health.
Medical professionals use muscle biopsy testing to confirm CoQ10 levels because muscles possess high CoQ10 content. The procedure requires specialists to extract a tiny piece of muscle tissue through a thigh cut under anesthesia. Doctors also recommend genetic screening to identify DNA variations linked to CoQ10 manufacturing processes.
The healthcare provider employs diagnostic procedures and clinical symptom assessments to establish a diagnosis. Inform your doctor about all the medications you take, especially statins, because these drugs interfere with CoQ10 level measurements.
Also Read: How Much Coenzyme Q10 Should You Take Per Day?
CoQ10 deficiency treatment
Coenzyme Q10 deficiency treatment proceeds through oral supplementation, yet daily doses usually extend between 100 and 1200mg, based on the condition's severity and cause. The supplement exists in two types: ubiquinone and ubiquinol, and the latter provides better availability, specifically for seniors.
You should take CoQ10 supplements with food that contains healthy fats to boost absorption. Healthcare providers frequently suggest distributing daily doses in smaller portions, which patients should take throughout the day. The supplement typically gets used with other treatments for patients with genetic conditions limiting their CoQ10 production abilities.
By administering higher doses, medical supervision becomes essential for treating primary CoQ10 deficiency syndromes among children. Symptom improvement occurs within weeks to months when medical supervision performs regular blood testing to adjust the dosage.
To support their treatment, people who supplement with CoQ10 should include fish, organic meats, and whole grains in their diets. Exercise has the potential to enhance cellular energy output and CoQ10 functional effectiveness in the body.
Conclusion
Identifying CoQ10 deficiency proves essential because of various symptoms, including anxiety, insomnia, dry eyes, and damage caused by statin medications. Strategic treatment plans require diagnosis of primary and secondary coenzyme Q10 deficiencies.
Medical practitioners use early diagnosis to develop successful treatment plans incorporating supplementation, dietary alterations, and lifestyle modifications. Individuals who access information about CoQ10 testing and treatment methods enhance their ability to control their CoQ10 balance, which leads to better overall wellness.
About WOWMD Staff
The WOWMD Staff category features a diverse team of writers, each bringing specialized knowledge in areas such as nutrition, fitness, wellness, and more. Articles in this category benefit from insights provided by multiple experts. All content is peer-reviewed and regularly updated to ensure compliance with our editorial standards.
References
- Coenzyme Q10 and its symptoms: https://www.cibdol.com/blog/1539-what-are-the-symptoms-of-needing-coq10
- What is Coenzyme Q10?: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Coenzyme_Q10
- Signs and symptoms of Coenzyme Q10 deficiency: https://advancedsofttissuerelease.com/7-signs-symptoms-of-coenzyme-q10-deficiency-treatment-research-studies/
- CoQ10 and Statins: https://www.healthline.com/health/coq10-and-statins
- Molecular genetic testing: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK410087/
Evidence Based Research
This WOWMD content has been reviewed, as well as checked for facts, so as to guarantee the best possible accuracy.
We follow a strict editorial policy, especially related to the sources we use. Our articles are resourced from reputable online pages, with research drawn from academic institutions and peer-reviewed studies. You can click on the numbers in the parentheses (1, 2, etc.) and check out those references.
The feedback form on this page can be used to report content that is not accurate, up-to-date or questionable in any manner.
We do NOT intend for the information presented through our articles to replace the medical relationship with a qualified physician, nor does it represent specialized advice.



 Skin Detoxification Bundle
Skin Detoxification Bundle Complete Weight Loss Bundle
Complete Weight Loss Bundle Heart Care Bundle
Heart Care Bundle Better Immunity Bundle
Better Immunity Bundle  Men's Immunity & Prostate Health Bundle
Men's Immunity & Prostate Health Bundle Stress + Energy + Wellness Combo
Stress + Energy + Wellness Combo  Energy Booster Combo
Energy Booster Combo Natural Skin Care Bundle
Natural Skin Care Bundle Workout Supplements Combo
Workout Supplements Combo Cognitive Health & Vision Combo
Cognitive Health & Vision Combo Joint Health Support Combo
Joint Health Support Combo

















 By WOWMD Staff
By WOWMD Staff